
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_How_operating_expenses_and_cost_of_goods_sold_differ_Sep_2020-01-558a19250f604ecabba2901d5f312b31.jpg)
They purchased 500 widgets at $10 per unit on March 3 and another 500 widgets at $13 each on September 9.Īt the end of the year, they have 25 widgets in inventory. Once you know the physical quantities of your various inventory items, you need to determine a method to assign them inventory costs.Īssume Paul’s Plumbing purchases 1,000 widgets during the year. Your inventory includes your stock of products, parts, and materials. Determine Cost to Assign to the Quantity on Hand An inventory aging report is a great tool for helping to identify items that have been in inventory for an extended period of time. Be sure to remove from physical inventory any items that are obsolete and unlikely to be sold. Taking a physical inventory helps you to determine the accurate quantity on hand. This count is usually performed at the end of the reporting period. Take a Physical InventoryĪ physical inventory is a method of manually counting your inventory and comparing it against recorded numbers. Theft and damage to products are the primary reasons for differences between the inventory on the books and what’s actually in the warehouse.
#Cogs cost of goods sold software
Don’t assume that what your accounting software reports matches exactly what you have in the warehouse. It’s a good idea to take a physical inventory count at least once a year, if not more.
This is the total cost of all the items in your inventory at the end of the year. Step 2: Determining the Cost of Ending Inventory The sum of all these costs incurred during the year makes up the inventory costs in the above formula. Overhead costs for administrative offices, retail space, or showrooms aren’t inventory costs. These include the shipping costs necessary to receive your materials and supplies, as well as overhead costs like rent, water, and electricity for the building or area where the products are assembled or manufactured. This doesn’t include costs for employees in finance, marketing, sales, or any other administrative areas.
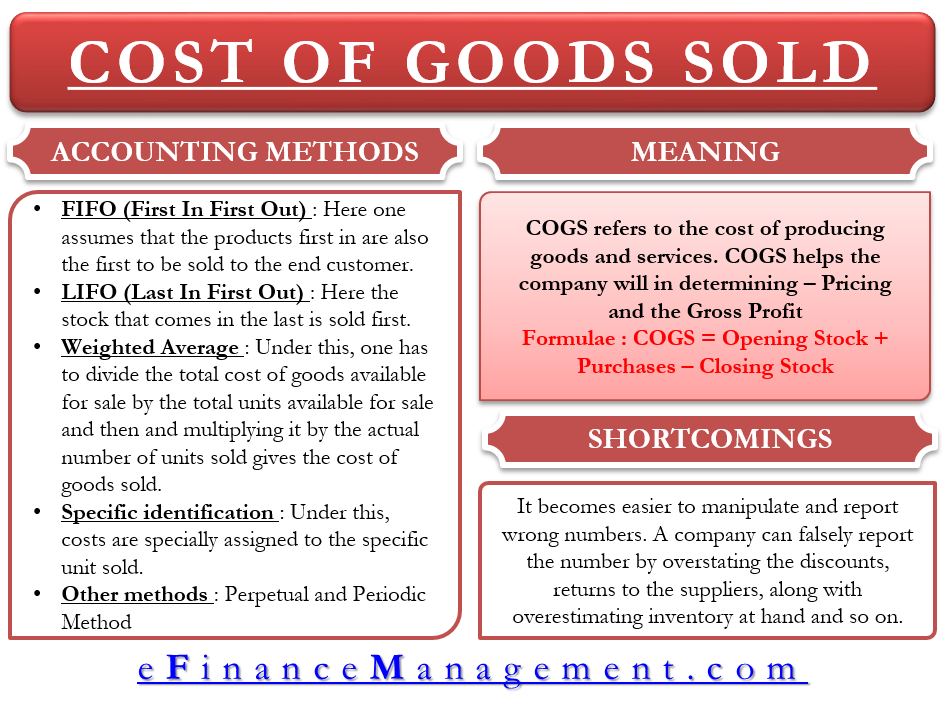

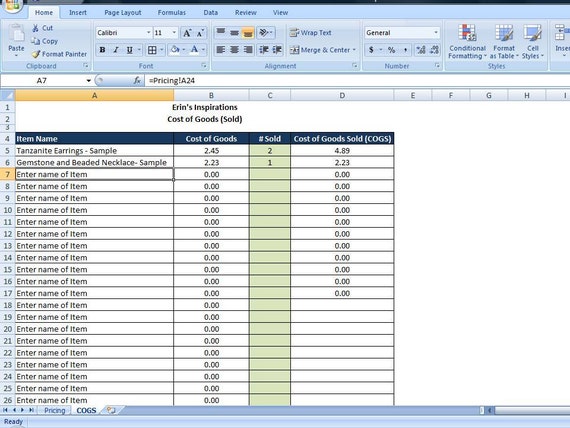
This is the cost of paying employees who work on creating your products. They have to be directly related to the production of your goods. This is the cost of materials and supplies needed to manufacture your product. This is the total amount spent for the products you placed in your inventory for selling purposes. The costs that go into calculating the cost of inventory are the cost of purchases, cost of materials, cost of direct labor, and other costs. Inventory costs aren’t only the prices paid to purchase items, but also the cost of storing and maintaining those items for however long it takes it to sell them. Calculating and tracking your cost of goods sold is one of the most important tasks of a bookkeeper in order to make sure your business is profitable.Ĭost of goods sold can be calculated by subtracting the ending inventory amount from the sum of the beginning inventory and inventory costs.ĬOGS = (Beginning Inventory + Inventory Costs) – Ending Inventory Step 1: Determining Inventory Costs It doesn’t include indirect expenses such as distribution costs and marketing costs. This includes the cost of any materials used in production as well as the cost of labor needed to produce the goods. Cost of goods sold (COGS) is an accumulation of the direct costs that go into the goods sold by your company.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
